Verifying the validity of the currency consumers handle daily is a crucial detail for both purchasers and the businesses in which they spend. The U.S. government has incorporated several advanced security features in Federal Reserve Notes (FRNs) to combat counterfeiting and ensure the authenticity of money.
Familiarity with these verifications can protect both the general public and banking industry professionals such as tellers, who must daily assess U.S. currency with an expert eye.

A Breakdown of U.S. Currency Security Features
1. Inspecting Bills: The Basics
- Paper Composition
- Portrait Design
2. Key Security Features of Money
- Watermark
- Color-Shifting Ink
- Security Thread
- 3D Security Ribbon ($100 Bills Only)
- Microprinting and Other Features
3. Investigating Additional Currency Indicators
- Serial Numbers and Federal Reserve Indicators
- Note Position and Plate Numbers
Inspecting Bills: Start with the Basics
Paper Composition
U.S. currency paper is a blend of 25 percent linen and 75 percent cotton, embedded with small, randomly placed, red-and-blue security fibers. The unique composition is difficult to replicate, making it a worthy first layer of security.
Portrait Design
The 2004-style FRNs feature an enlarged, off-center portrait without a frame. This design change from earlier styles not only modernizes the appearance but also makes it harder for counterfeiters to produce exact replicas.
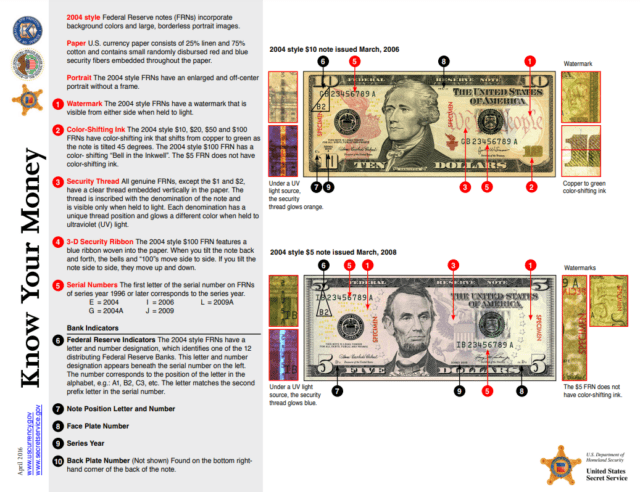
Money’s Key Security Features
Watermark
One of the most prominent security features is the watermark. Visible from both sides when held to light, the watermark is a faint image that matches the bill’s portrait. For instance, the 2004-style $100 note includes a watermark of Benjamin Franklin to the right of his image.
Color-Shifting Ink
The color-shifting ink used in the 2004-style $10, $20, $50, and $100 FRNs changes from copper to green when the note is tilted 45 degrees. This effect is most noticeable on the numeral in the lower right corner of the front of the bill.
The $100 note has a specific use of this color shift technology, applying it to a bell in an inkwell to the bottom-right of Franklin’s face. This security feature is therefore known as the “Bell in the Inkwell.”
Security Thread
All genuine FRNs, except the $1 and $2 denominations, contain a clear security thread embedded vertically in the paper. This thread is inscribed with the note’s denomination and can only be seen when held to light. Under ultraviolet (UV) light, the thread glows in different colors, depending on the denomination:
- $100: pink
- $50: yellow
- $20: green
- $10: orange
- $5: blue
3D Security Ribbon
Exclusive to the $100 FRN, a blue ribbon woven into the paper exhibits an interactive effect. When tilting the note back and forth, the bells and “100s” on the ribbon move side to side; tilt it side to side, and they move up and down.
Microprinting and Other Features
Microprinting — small printed text that is difficult to reproduce accurately — appears in various places on the notes. For example, the words “The United States of America” are seen in capital letters and appear around the portrait of the $100 note.
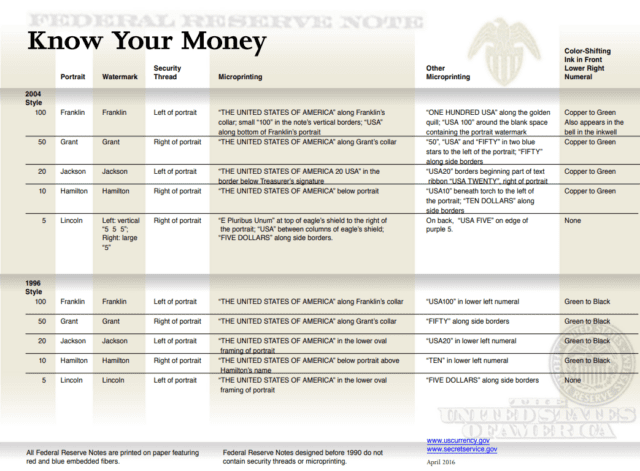
Investigating Additional Indicators of Currency
Serial Numbers and Federal Reserve Indicators
The first letter of the serial number on FRNs indicates the series year. For example, “E” represents the 2004 series.
Each note also has a letter and number designation identifying one of the 12 Federal Reserve Banks, which appears beneath the serial number on the left side.
Note Position and Plate Numbers
Each note includes a note position letter and number, face plate number, and back plate number (found on the back of the note in the bottom right-hand corner). These features aid in identifying the specific print run and position of the note on the printing plate.
Ensuring Authenticity
Understanding and recognizing these security features is essential for ensuring the authenticity of U.S. currency. Prudent bank tellers should know these features in detail to better protect both customers and the bank itself.
The following online sources have additional details on U.S. currency security features: